Blockchain Commons produces projects that fulfill its Vision.
Much of this centers on an Architecture that focuses on our Gordian Principles of independence, privacy, resilience, and openness and that encourages responsible key management. This Architecture is built upon Specifications that have been created in conjunction with the Wallet Community. Developer Support enables the usage of these specifications, while Reference Apps further demonstrate that usage.
Beyond its architectural core, Blockchain Commons also supports Events, Educational Projects, and Advocacy Projects.
The Gordian Architecture
Overview: Architecture, Principles, Roles
Topics: Why CBOR?, Progressive Trust Life Cycle
Articles: Musings of a Trust Architect
The Gordian Architecture is the heart of Blockchain Commons’ work. It’s a partitioned architecture and a set of backup, communication, and encoding specifications, built to support the Gordian Principles.

The Gordian Architecture supports users through those four principles.
- Independence. The Gordian Architecture supports self-sovereign control of digital assets. Users are in control, not centralized organizations.
- Privacy. The Gordian Architecture is privacy-protecting, allowing selective protection and disclosure of data.
- Resilience. The Gordian Architecture focuses on #SmartCustody to eliminate Single Points of Failure and Compromise; controlling your own assets can be tricky, and the Gordian Architecture makes it as safe as possible while also maximizing security.
- Openness. The Gordian Architecture helps developers to come together using open specifications that allow interoperability.
The Gordian Architecture is a future-looking design that covers everything that from the high-level architecture of a Gordian ecosystem through the specifications and UX best practices that make it possible. It allows blockchain, wallet, and web developers to deploy fully featured applications that incorporate all the current best practices of the digital-asset community.
Gordian Specifications
The Gordian architecture is built on specifications that empower our Vision. These specifications are what create the independence, privacy, resilience, and openness of our designs. They are broken into three main categories: the core stack, the UX stack, and the crypto stack.
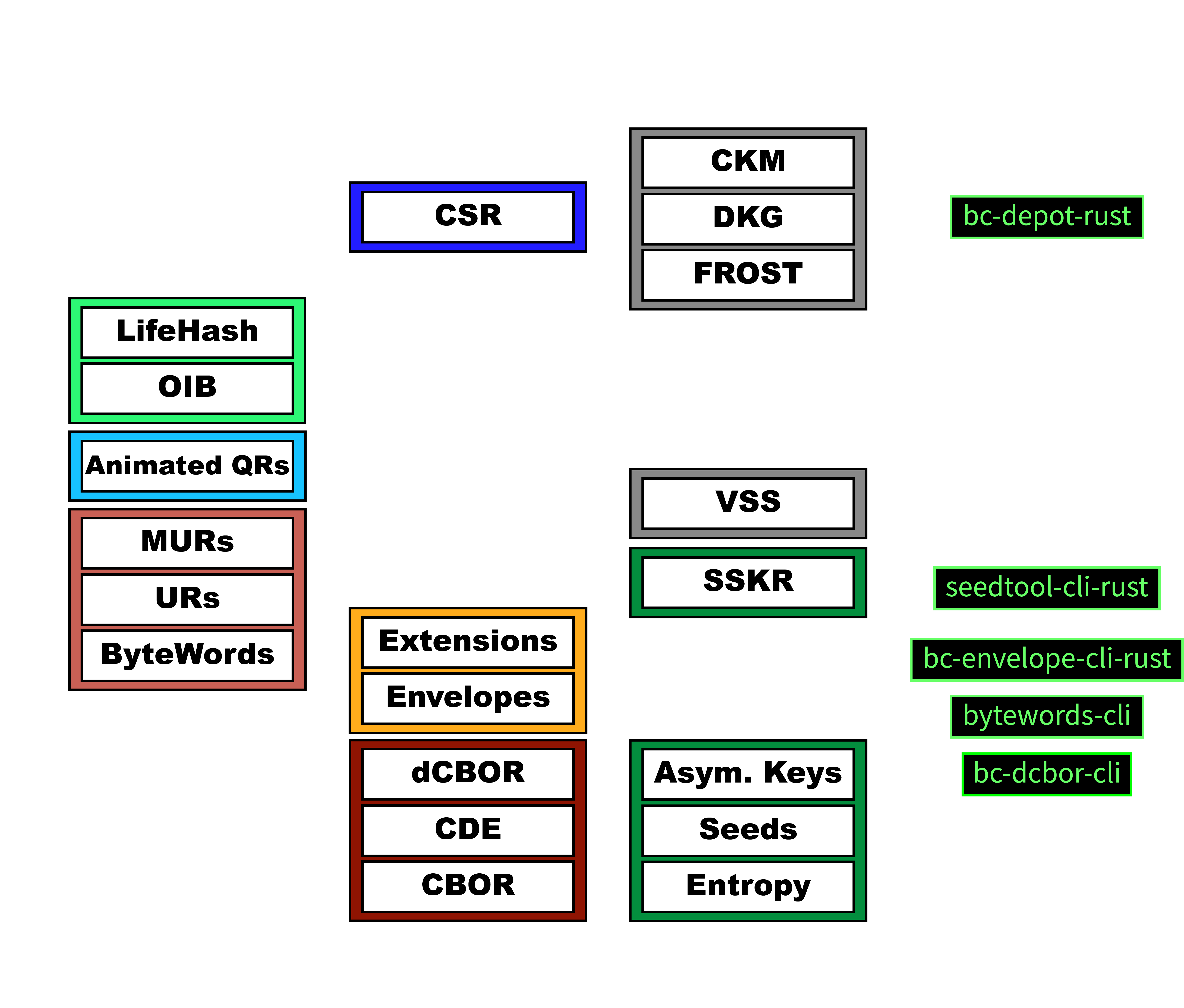
Core Stack Specifications
- Identifiers: Cliques, Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), XIDs
- Collaborative Seed Recovery: CSR
- Blockchain Commons Depo: bc-depo-rust
- Depo API: bc-depo-api
- Envelope: Envelope, Request/Response, Gordian Sealed Transaction Protocol (GSTP), Encrypted State Continuations (ESC)
- Envelope IETF Draft: Envelope I-D
- Introduction to Envelope Videos: Teaser, Understanding Envelope, Understanding Extensions
- CBOR: dCBOR
- dCBOR IETF Draft: dCBOR I-D
Blockchain Commons’ Core Stack includes its major user-facing innovations, as well as the foundational encoding that allows them:
- Identifiers support SSI by allowing users to control their identity.
- Collaborative Seed Recovery (CSR) is a system intended to improve the resilience of seeds and other digital assets by allowing them to be split up and then stored on a variety of share servers.
- Envelope allows for the compact storage and transmission of data, as well as hashed elision and encryption.
- dCBOR defines a deterministic version of CBOR, crucial for a variety of tasks including the hashed storage of data.
UX Stack Specifications
- Object Identity Block: OIB, LifeHash
- Lifehash Explainer Video: Video
- Lifehash Website Demo: Lifehash.info
- Uniform Resources: ByteWords, URs. Animated QRs
- Multipart URs: MUR Implementation Guide
Blockchain Commons’ OIB helps users to identify digital assets:
- OIB is a standardized block of info to identify a digital asset.
-
Lifehash LifeHash is a method of hash visualization that creates beautiful icons that are deterministic, yet distinct and unique given the input data. Blockchain Commons UR stack allows for the encoding of CBOR binary strings as text strings or as QRs:
- Bytewords is a method for encoding binary data as four-letter words, used by URs.
- URs underlie Envelope and Animated QRs and ensure interoperability.
- Animated QRs support the transmission of larger amounts of data across air gaps.
Crypto Stack Specifications
- CKM: CKM, FROST, MuSig2
- FROST Implementer Meetings: November 2023, September 2024
- FROST Developer Meetings: April 2024, December 2024
- Sharding: SSKR
- SSKR Security Review: 2021 Review
- SSKR Security Review: 2021 Review
The Crypto Layer supports the resilience and independence of digital assets through cryptographic protections that allow users to use and maintain those assets.
- CKM is a next-generation system of collaborative key management.
- FROST is one of the multi-sig methods that could be used for CKM.
- MuSig is another multi-sig method that can be used for CKM.
- SSKR is Sharded Secret Key Reconstruction, which is our current methodology for sharding and reconstructing a key.
Research Papers
Repo: Research
Video: Overview
Most of our specifications begin with “BCR” Research papers, which describe and detail the use of new, interoperable specifications for blockchain and Bitcoin. The ultimate goal is to upgrade BCRs to BCPs when they come into use by multiple parties, then to turn them into specifications.
Gordian Developer Support
The Blockchain Commons repos include libraries and apps that help developers to develop and test the Gordian specifications.
Open Integrity

Repo: Open Integrity Project
Documents: Architecture, Problem Statement, Script Snippets
Open Integrity seeks to increase the trust of Git repos by creating a foundational root of trust with an inception commit and by creating a chain of trust from that point, allowing the rotation of keys and authorized users. It does so with scripts and aliases that don’t replace Git, but instead supplement it. This is something that we recommend for all developers.
Developer Libraries
Developers: Library Listing
Reference libraries demonstrate the use of our specifications. They were originally coded in C or C++, and some have been recoded by us in Rust and Swift. Other developers have also produced conversions for Java, Python, and other languages.
CLI & Web Apps
Developer Resources: Developer Website
CLI Apps: Bytewords-CLI, dCBOR-CLI, Envelope-CLI-Rust, LifeHash-CLI, Provenance-Mark-CLI-Rust, Seedtool-CLI-Rust
Older CLIs: Envelope-CLI-Swift, Keytool-CLI, Musign-CLI, Seedtool-CLI-Swift
iOS Apps: URDemo
Web Apps: lifehash.info, seedtool.info, Spotbit
Apps for the command-line and for iOS and the web can aid developers in testing out their work.
Gordian Reference Apps
Whereas Developer Apps are meant for testing, the Gordian Reference Apps offer best practices and examples of how to incorporate Reference Libraries into applies that support the Gordian Principles.
Gordian Depo (CSR)
Repo: Depo
API: Depo API
Introduction: CSR Overview
CSR Architecture: Architectural Overview
Next Step: CKM Overview
Collaborative Seed Recovery, or CSR, automates the recovery of seeds and other sensitive digital data in a way that is safe, secure, and simple to use. It manages this by sharding secrets and then storing shares on different servers. This is not a methodology to prevent compromise, but simply to add resilience to recovery in the case of failure or loss. It is an exemplar for how to introduce a key management role into a Gordian Architecture.
Blockchain Commons’s reference app for CSR is built on the SSKR library and the Depo Server, which uses the Depo API for communication. We expect other partners will use different servers for their share storage.
Gordian Seed Tool (iOS)
Repo: Seed Tool
Blog: Gordian Seed Tool Reveals the Foundations of Cryptography (7/15/21)
Gordian Seed Tool is Blockchain Commons’ most fully featured reference app. It demonstrates independence and resilience by protecting your cryptographic seeds while also making them available for easy use. Using Seed Tool, you can generate seeds and store them securely on your device. You can then derive and share multi-signature signing and verification keys from those seeds or alternatively sign PSBTs directly from the app. Sophisticated backup procedures demonstrate the usage of Sharded Secret Key Reconstruction (SSKR) — which lets you split your seed into pieces and send them to trusted parties, who can send them back to you in an emergency for seed recovery. You can even use an entirely offline device (no internet access) to store your seeds and use QR codes to exchange necessary information with online devices running compatible wallet or signing software. A complete manual details its functionality.
Gordian Server (MacOS)
Repo: Gordian Server
Gordian Server installs a self-sovereign Bitcoin Core server, protected by Tor, on your Mac computer. This gives you complete control over your Bitcoin destiny, and supports easy connectivity with Gordian Wallet, Fully Noded, and other wallets that support the QuickConnect API.
Other Gordian Reference Apps
Legacy Repos: Coordinator, Cosigner iOS, Cosigner Android, or Cosigner macOS, Wallet
Hardware Repos: Lethekit
Research Repos: Mori-CLI, Sweeptool
Several other reference apps have been released to demonstrate specific Principles. Some of these apps have since become outdated or superceded by other applications. Several research reference apps have been written to test out new technologies and new ways to demonstrate our Vision, but haven’t been upgraded to full reference status.
Events
One of the prime goals of Blockchain Commons is to bring together different parties to educate and to create consensus on the future development of our technologies and specifications. This happens through events.
Gordian Meetings
Meetings Website: Meetings List Announcements List: Sign Up
Blockchain Commons holds monthly meetings, usually on the first Wednesday of the month, that support wallet developers in advancing their work in an interoperable way. There are often discussions of updates to interoperable Blockchain Commons technologies, plus special presentations from other developers in the field highlighting their own work and advancements.
FROST Round Table
FROST Website: Developers FROST
Intro: A Layperson’s Intro to Schnorr
Implementer Round Tables: November 2023, September 2024
Developer Meetings: April 2024, December 2024
FROST is a threshold signature scheme for Schnorr signatures that provides a next-generation resilience methodology for the control of digital assets. Blockchain Commons has run a series of meetings to support its roll-out. Impementer Round Tables have brought together experts in the field and allowed them to discuss the challenges of implementation. Developer Meetings have supported wallet cerators in incorporating FROST into their own work.
Silicon Salon
Website: Siliconsalon.info
The Silicon Salon seeks to create semiconductor solutions for cryptography by bringing together semiconductor manufacturers who are interested in creating silicon solutions specifically intended for cryptography with wallet creators and other cryptographic principals. Each event to date has included presentations from principles in the area and discussion among attendees. Our web site includes the presentations and summarizes the discussions.
Rebooting the Web of Trust
Website: weboftrust.info
GitHub Repos: WebofTrust Repos
Rebooting the Web of Trust is a semiannual design workshop that was founded by Christopher Allen prior to the foundation of Blockchain Commons; many of its ideas in turn became the heart of our initial work. We continue to attend and support the workshops.
Educational Projects
Educational projects consist of books, tutorials, or courses, intended to teach the usage of blockchains to programmers and end users alike.
Learning Bitcoin from the Command Line
Repo: Learning-Bitcoin-from-the-Command-Line
Future: Topics for v3.0
Blog: Learning Bitcoin Upgrades to v2 (10/30/20)
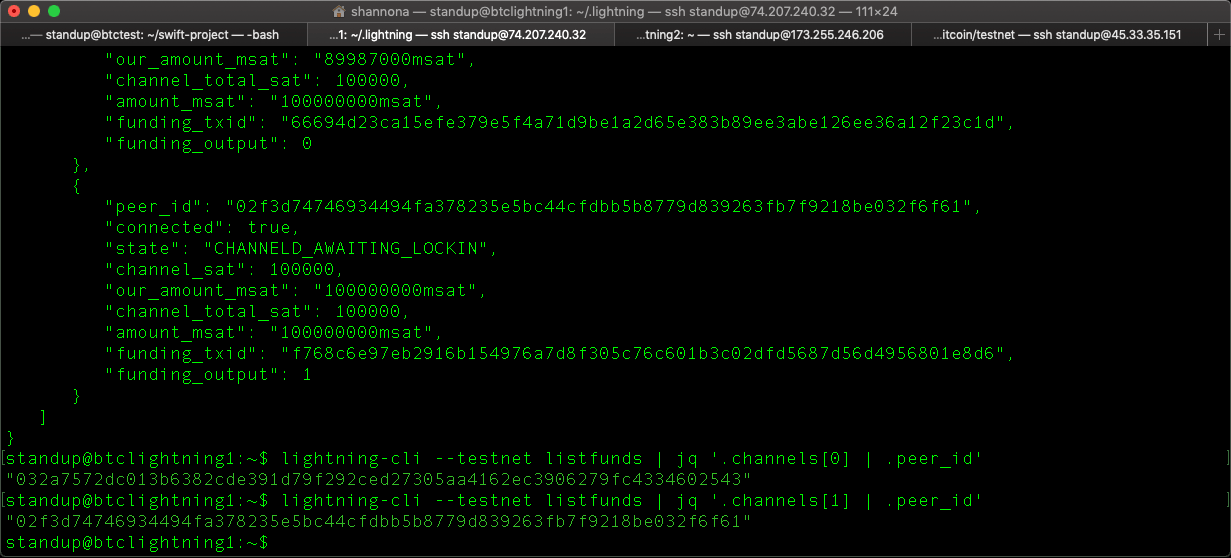
This is a complete twenty-chapter course intended to teach system administrators, developers, and engineers who are already acquainted with the UNIX command line interface how to work with Bitcoin. It uses this methodology to teach the fundamentals of Bitcoin, from RPC communications to how transactions work and how scripts work. The majority of the course is focused on bitcoin-cli, but there’s also information on scripting, on programming with the RPC interface, and on using other command-line programs, beginning with lightning-cli. Translations are now available for Portuguese, with the final iteration of Spanish pending.
#SmartCustody
PDF: #SC v1.01
Book Site: WWW Site
New Scenarios: Multisig Scenario
New Technologies: Articles
Case Studies: Overview
Repo: SmartCustody Repo, SmartCustodyBook
Future: Outline for v2.0
Blog: June TweetStorms on #SmartCustody Adversaries, 1-on-1 Advice, Supporting Smart Custody Book v2 (6/3/20)
The Use of Advanced Cryptographic Tools to Improve the Care, Maintenance, Control, and Protection of Digital Assets. This five-chapter (186-page) book is intended to make you rethink the security of your digital assets. It puts together a risk-modeling system with two additional building blocks: a cold-storage scenario for managing self-custody; and an extensively detailed list of potential adversaries. By working through the book, you can determine which adversaries are actually the most dangerous to your assets, and adjust your own self-custody scenario to accommodate them. Additional chapters talk about fiduciary duties with regard to digital assets.
A v2.0 of this book is in the planning stage, to improve the accessibility of the course, to support additional hardware tools, and to introduce multi-signature scenarios. Our multisig design article, our sharding design article, our SSKR Dangers article, Timelock exploration article, and our multisig scenario will all be incorporated into #SC 2.0 in some form, per our #SC 2.0 outline.
Advocacy Projects
Blockchain Commons isn’t just about technological development. It also works to ensure that there’s a solid legal foundation for our blockchain technologies. That’s where Advocacy comes in.
Law & Advocacy
Website: Law & Advocacy Website
Repo: Law & Advocacy Website Repo
Articles: Article Webpage
Repo: Testimony Webpage
Our Law & Advocacy repo includes both research that we’ve done on the current state of the law and advocacy that we’ve done to change that status.
How to Get Involved
Want to become involved in Blockchain Commons’ projects? Here’s how!
- Participate in the Gordian Developer Community. Join our meeting announcement lists and Signal groups.
- Contribute to Projects. Submit Issues to Projects or (even better) PRs, offering clear improvements. We welcome them on all our repos!
- Become a Sponsor. Support Blockchain Commons by becoming a GitHub Sponsor. We welcome all donations, as they allow us to continue our industry-supporting work. If you’re a company interested in becoming more involved, talk with us about becoming a Project Sponsor or a Sustaining Sponsor! We’re happy to work with you on your specific interests!

